By Garth W. Cane
Oil lubricates, cools, cleans, seals, and protects against rust and corrosion in our engines. A thin film of oil holds spinning parts away from stationary parts to prevent friction from metal to metal contact which could wear away the surface.
Oil is a petroleum distillate that comes from deep in the earth and is separated from other petroleum products by the refining process. Crude oil is heated in a cracking tower and products such as asphalt, diesel oil, heating oil, lubricating oil, gasoline, propane gas and chemicals for making plastics and other polymers are developed as large hydrocarbons are separated into smaller ones.
 Engine oil is towards the heavy end of the products coming from the crude oil, but it can contain a little of the lighter and heavier components. This is what causes some of the instability of conventional oil and allows it to break down quicker than a pure synthetic oil.
Engine oil is towards the heavy end of the products coming from the crude oil, but it can contain a little of the lighter and heavier components. This is what causes some of the instability of conventional oil and allows it to break down quicker than a pure synthetic oil.
Synthetic oil is manufactured instead of pumped from the underground. It’s made to be homogeneous and will protect and last longer than conventional oil. Synthetic oils are composed of molecules of uniform size and shape. It is used as a substitute for petroleum-refined oils when operating in extreme temperatures. All petroleum-based oils break-down in a hot engine, but synthetic oils have a higher tolerance to burn off on hot cylinder walls and pistons and can last much longer with the right filtration system.
Oil helps cool the engine by absorbing heat from moving parts and transferring it to the oil cooler in the radiator where it will be diffused into the surrounding air. The oil splashes on the bottom skirt of the pistons helping transfer the heat so that the pistons do not expand inside the cylinders. As you drive, small particles of grit enter your engine through the air cleaner where they could grind against any moving parts. Oil washes away these bits of metal, dirt, and other particles and deposits them in the oil filter where they can do no harm.
Proper lubrication reduces friction, helps to increase fuel economy and increases engine life by cushioning moving parts. It helps seal the piston rings and the cylinder walls to maintain compression and prevents air from coming in contact with the steel parts of the engine that would cause oxidation or rust on the parts.
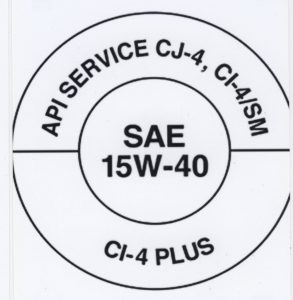
 When we buy oil for our engines we often are confused over the markings on the container. Some of the markings refer to American Petroleum Institute (API) service ratings, that range from SA for the lowest quality oil to the latest SJ synthetic oil for modern engines with turbochargers. An oil is rated for viscosity by heating it to a specified temperature, and then allowing it to flow out of a specifically sized hole. Its viscosity rating is determined by the length of time it takes to flow out of the hole.
When we buy oil for our engines we often are confused over the markings on the container. Some of the markings refer to American Petroleum Institute (API) service ratings, that range from SA for the lowest quality oil to the latest SJ synthetic oil for modern engines with turbochargers. An oil is rated for viscosity by heating it to a specified temperature, and then allowing it to flow out of a specifically sized hole. Its viscosity rating is determined by the length of time it takes to flow out of the hole.
The viscosity or oil weight is a measure of the fluidity of the oil, or its ability to flow. Higher numbers indicate a heavier oil and lower numbers like SAE 5 or 10 refer to oils that flow easily in colder weather. When cold, oil thickens and resists flowing. This could cause hard starting in cold weather and poor lubrication until the engine warms up. If oil becomes too thin when it gets hot, it cannot provide the lubrication that we need as it breaks down causing damage to moving parts. Multi-viscosity oils like 10W-30 act like a very thin easily flowing oil when the engine is cold, and act like a heavier duty oil to provide protection as the engine gets up to operating temperature.
We should always use the viscosity of oil recommended by the manufacturer of our engine, but some older high mileage engines benefit from a heavier weight oil to help seal and lubricate parts that have worn. This may also prevent oil from passing worn piston rings during deceleration when high vacuum can draw the oil into the combustion chamber where it burns showing a blue smoke in the exhaust, and sludge in the engine.
Synthetic oils are wax-free so that they flow better in colder temperatures. They contain additives that are better for combating breakdown (chemical changes) forming sludge which will block the small passages through the block and head that the oil must travel through to lubricate individual parts, preventing corrosion and gumming by oxidation, and foaming from air bubbles. Air will not hold moving parts away from each other. Synthetic oils often allow the engine and transmission to run cooler and allow more mileage between oil changes. Many new trucks and SUVs come from the factory with synthetics in the oil pan and the transmission.
Oils consist of about 30 per cent oil and the balance is made up from different additives. Most automotive engineers believe that there are enough additives in the best quality oils so that you do not need to buy extra additives from your local automotive distributor. Calcium and magnesium detergents in the oil help keep the engine clean, and dispersants keep sludge and dirt in suspension until it can be removed by the oil filter. Phosphorous and Zinc additives in synthetic oil are important to engines with turbochargers to maintain anti-wear lubrication after the engine shuts down. The high heat from the exhaust gases in a turbo can cook normal oils in its bearings as it spools down after the normal oil flow stops.
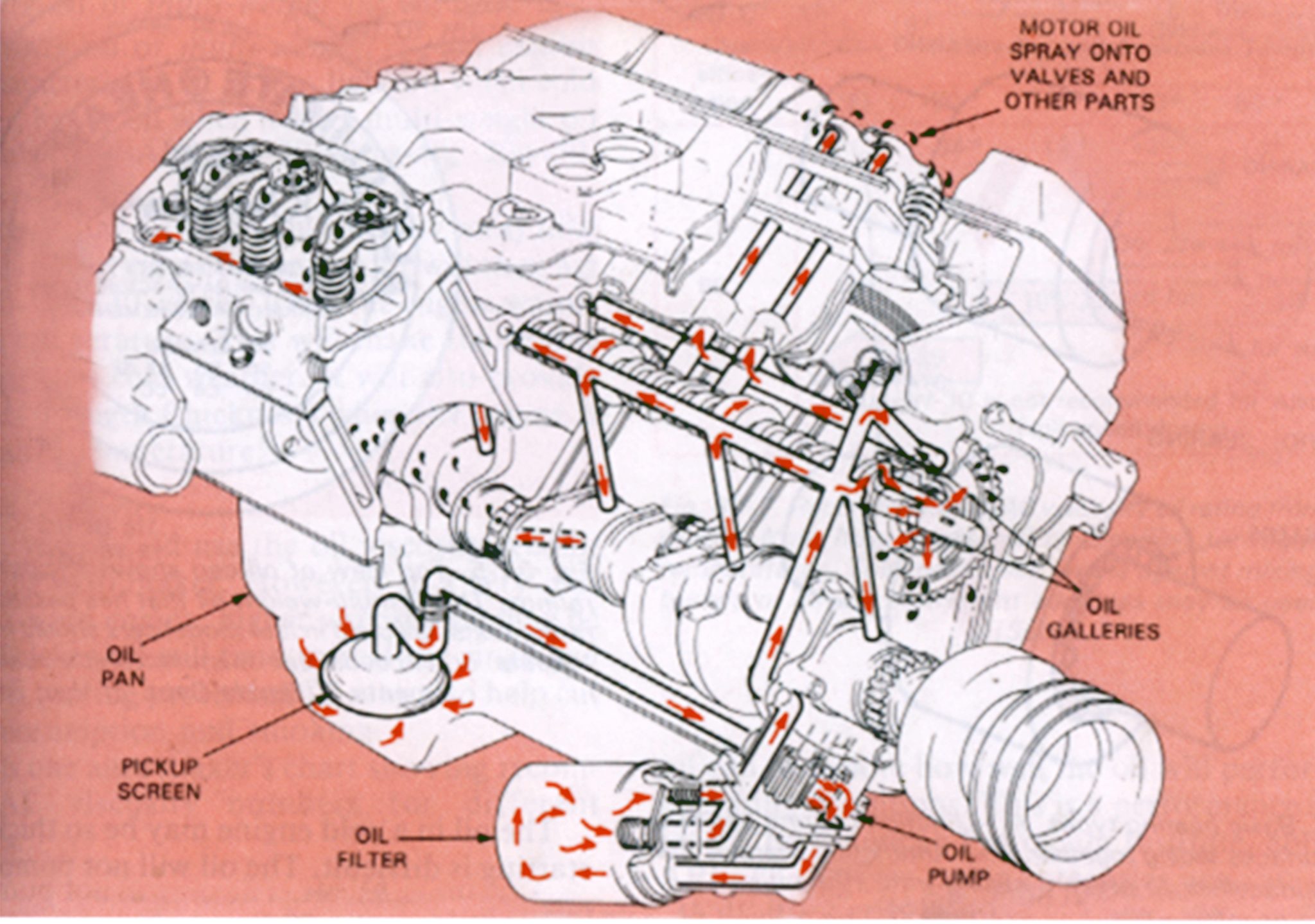 The oil pump supplies the crankshaft bearings, camshaft bearings, lifters, and rocker arm assemblies through a series of oil galleries. Oil is sprayed on the valves and splashed on the bottom of the pistons for cooling and lubrication of the connecting rod and wrist pin. The rings on the pistons clean the oil off the walls of the cylinder as the piston goes down so that the oil is not left to burn in the combustion chamber. If the valve guides become worn, then oil can migrate up the shaft of the valve where it can burn in the combustion chamber.
The oil pump supplies the crankshaft bearings, camshaft bearings, lifters, and rocker arm assemblies through a series of oil galleries. Oil is sprayed on the valves and splashed on the bottom of the pistons for cooling and lubrication of the connecting rod and wrist pin. The rings on the pistons clean the oil off the walls of the cylinder as the piston goes down so that the oil is not left to burn in the combustion chamber. If the valve guides become worn, then oil can migrate up the shaft of the valve where it can burn in the combustion chamber.
Oil filter elements are normally made from either paper or cotton to allow the oil to flow but block and trap small debris like small metal particles, carbon, rust and dirt. Bypass oil filters are commonly used to protect the engine from oil starvation if the filter element becomes clogged. When the oil pressure is too high, caused by cold or thick oil, the bypass valve will open allowing unfiltered oil to flow to the engine bearings, preventing major damage.
Oil coolers may be used to reduce the temperature of the oil in heavy duty engines and vehicles with a trailer towing package. The oil is pumped through a radiator like device so that the excess heat can be driven off by a strong flow of air as you drive. If your vehicle is not moving down the road, the only air flow that is provided is from the radiator fan- this may not be enough to cool your oil.
The positive crankcase ventilation system (PCV) draws toxic fumes out of the engine crankcase and burns them in the combustion chamber. This helps prevent sludge formation that could restrict the oil circulation in the galleries and pollute the atmosphere with vapors.
 The top of the engine is the last section to receive oil from the pump, so many race cars have the top of the engine disassembled before a race so that the upper cylinder parts may be lubricated before the engine is started. Some companies offer a pre-lubricator for heavy duty diesel motorhome engines to send oil up to the top of the engine before the engine is started. This is run by a 12-volt pump.
The top of the engine is the last section to receive oil from the pump, so many race cars have the top of the engine disassembled before a race so that the upper cylinder parts may be lubricated before the engine is started. Some companies offer a pre-lubricator for heavy duty diesel motorhome engines to send oil up to the top of the engine before the engine is started. This is run by a 12-volt pump.
Some automotive manufacturers recommend staying with the same brands of oil since different additives may be used by different companies. Shell Rotella has introduced a new synthetic oil formulated for gas engines in SUVs and trucks that provides extreme protection for towing and hauling. These oils offer unsurpassed protection for these engines with three viscosity grades; 0w-20,5w-20,and 5w-30 .
You should check your oil at least once a month when the vehicle is on a flat surface when the engine is cool and has been shut down for a time. This allows the oil to drain back down into the sump where the level is measured. Look at the oil on the dipstick to be sure that it is clear and does not have a burned smell. It will be darker than the new oil you pour into the engine as its job is to remove dirt.
If your engine does not use some oil, then the parts may not be getting the lubrication it needs.























